The Houthis, a Yemeni militia backed by Iran, launched a campaign against Israel shortly after the Gaza war erupted on Oct. 7, 2023. During the first nine months of the conflict, they fired more than 200 cruise missiles, ballistic missiles and drones at Israel. The Houthis primarily targeted Eilat, the strategic Israeli port on the Red Sea that is roughly 1,000 miles from Sanaa. Only one cruise missile hit Israel, although it did no damage. A drone suicide drone killed one person in Tel Aviv. The Houthis, which began as a religious revival movement among Zaydi Shiites, have repeatedly vowed to continue attacks until the Gaza war ends in solidarity with Hamas.
“The Houthis will not hesitate to expand their military operations against the Israeli entity to include targets that they do not expect on land or at sea,” Houthi spokesperson Yahya Saree said in November 2023. The rhetoric has intensified as the Israeli campaign made military gains in Gaza. The Houthis pledged to escalate unless the “siege” of the Palestinians ended.
Most of the Houthi weapons were reportedly shot down by Israeli aerial defense systems or fell short. U.S. and French warships in the Red Sea also downed some of the Houthi missiles and drones headed toward Israel. Saudi Arabian air defenses also reportedly intercepted two missiles. Israel did not appear to counterstrike the Houthis for the first nine months of the war.
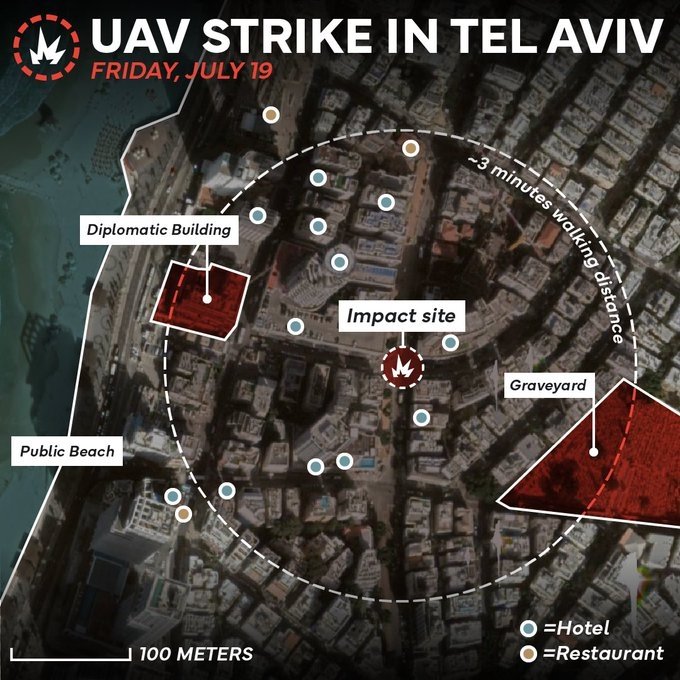
Tensions escalated on July 19, 2024, when a Houthi suicide drone hit an apartment building near the beach in Tel Aviv, killing one person. The long-range attack from Yemen was unprecedented. The upgraded Samad-3 drone took a circuitous route to Israel to avoid detection. Israel responded with strikes on the strategic Red Sea port of Hodeidah on July 20.
The Houthis have espoused anti-Israeli and anti-American views since the movement emerged in the 1990s. Their slogan is “God is great. Death to the U.S. Death to Israel. Curse the Jews. Victory for Islam.” Known as Ansar Allah (or Supporters of God), the Houthis are a minority in Yemen.
Iran provided the Houthis with light arms, rockets and anti-aircraft missiles, which were originally used to fight the Saudi-backed government in Yemen in six wars between 2004 and 2010. The Houthis seized control of Sanaa, the capital, in 2014, forcing the central government into exile in Saudi Arabia. Tehran provided increasingly advanced cruise and ballistic missiles and drones capable of reaching Israel after Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates opened an air war in 2015.
The campaign against Israel was part of a wider Houthi campaign during the first nine months of the Gaza war that included dozens of strikes on commercial shipping and naval warships, including U.S. Navy ships, in the Red Sea. The Houthis initially claimed that they were targeting commercial ships on their way to or linked to Israel to show solidarity with Palestinians in Gaza, although the attacks hit vessels linked to more than 50 nations.
The Houthis offensive overlapped with attacks by other militias in the so-called “Axis of Resistance,” a network of militias in the Palestinian territories, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq and Yemen fostered and armed by Iran. “We are in a multi-front war,” Defense Minister Yoav Gallant said in December 2023. “We are being attacked from seven different arenas.”
The Houthi threat from the south was small compared to the more than 5,000 rockets launched by Hezbollah from Lebanon across Israel’s northern border during the first eight months of the regional conflict. The following are attacks by the Houthis on Israel since the start of the Gaza war.
Oct. 19, 2023: The Houthis fired cruise missiles and several drones potentially headed toward Israel. The USS Carney intercepted four missiles and 15 drones over the Red Sea.
Oct. 27, 2023: The Houthis launched two drones toward Israel. One hit a building next to a hospital in the Egyptian town of Taba near the border with Israel in the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt's military downed a second drone before it entered its airspace. The debris fell near the town of Nuweiba.
Oct. 31-Nov. 1, 2023: The Houthis launched ballistic missiles and drones toward Israel. Israel intercepted multiple incoming projectiles. An Arrow 2 battery intercepted a surface-to-surface missile for the first time.
Nov. 9, 2023: The Houthis launched a surface-to-surface ballistic missile aimed at Eilat. It was intercepted by Israel’s Arrow defense system over the Red Sea. Another “suspicious target” was intercepted by a Patriot battery.
Nov. 14, 2023: The Houthis fired a surface-to-surface missile toward Eilat, but Israel intercepted it over the Red Sea with the Arrow system.
Nov. 22, 2023: The Houthis fired a cruise missile over the Red Sea toward Eilat. It was intercepted by Israel.
Dec. 6, 2023: The Houthis launched a ballistic missile toward Eilat. It was intercepted by Israel's Arrow defense system.
Dec. 26, 2023: The Houthis fired drones toward Israel. Israel intercepted one projectile over the Red Sea by Israeli aircraft. U.S. forces shot down 12 drones, two land attack cruise missiles and three antiship ballistic missiles.
Feb. 2, 2024: The Houthis launched a surface-to-surface ballistic missile at the southern port city of Eilat. It was intercepted by Israel‘s Arrow aerial defense system over the Red Sea.
March 18, 2024: The Houthis fired a cruise missile that landed outside Eilat. It was the first time the Houthis struck Israeli territory.
March 21, 2024: Israel intercepted a suspicious aerial target near Eilat that came from the direction of the Red Sea.
April 8, 2024: A hostile aircraft approached Eilat from the south. Israel's C-Dome, a ship-mounted defense system, downed the target. The system had not previously been used in combat.
April 13-14: The Houthis reportedly launched dozens of drones and missiles at Israel from al Jawf and al Baydha Governorates in central and eastern Yemen. At the same time, Iran launched an unprecedented attack on Israel with 185 suicide drones, 110 ballistic missiles and 36 cruise missiles. Iran's militia allies in Lebanon, Syria and Iraq also fired munitions at Israel. The swarm of assaults were retaliation for Israel’s airstrike, on April 1, on an Iranian diplomatic mission in Damascus that killed three Revolutionary Guards generals as well as other military officials.
June 3, 2024: Israel’s Arrow system intercepted a ballistic missile that was reportedly fired at Eilat by the Houthis.
June 6, 2024: The Houthis claimed to have launched two attacks in coordination with the Islamic Resistance in Iraq, an umbrella of Iran-backed militias, on three ships in Israel’s Haifa port. IDF spokesperson Lieutenant-Colonel Peter Lerner denied the claims.
June 12, 2024: The Houthis and the Islamic Resistance in Iraq claimed to have launched a missile and drone attack on targets in Ashdod and Haifa, two of Israel’s three main cargo ports.
June 22, 2024: The Houthis and the Islamic Resistance in Iraq claimed to have launched a coordinated drone attack on two cement tankers and two cargo ships at the port of Haifa. Israeli media reported an explosion in Haifa and Israel’s military reported shooting down a drone launched towards Israel from the east.
June 26, 2024: The Houthis and the Islamic Resistance in Iraq claimed to have launched drone attacks on targets in Haifa and Eilat as part of a joint military operation. The IDF acknowledged that a drone exploded near Eilat but did not report anything unusual in Haifa.
July 2, 2024: The Houthis and the Islamic Resistance in Iraq reportedly attacked a target in Israel’s Haifa port using “several winged missiles.”
July 8, 2024: The Houthis claimed to have launched a successful drone attack on Eilat in coordination with the Islamic Resistance in Iraq. The IDF said that its jets had intercepted a suspicious target approaching from the south before it crossed into Israeli territory.
July 14, 2024: The Houthis claimed an attack on unspecified military targets in Eilat using drones.
July 19, 2024: The Houthis launched a modified Samad-3 drone that traveled some 1,000 miles from Yemen to Israel. It came from the West and then exploded near the U.S. Embassy branch office in Tel Aviv, killing one person. Israel attributed the failure to intercept the drone to human error. The Houthis claimed responsibility and said that the drone was a new model called the Yaffa, which could not be detected by radar. The IDF intercepted a second drone that came from the East around the same time.
July 20: Israel launched airstrikes on the Red Sea port of Hodeidah in Houthi-controlled territory in western Yemen. The IDF said that it targeted gas and oil depots, a power station, and military sites. The port was used to import aid as well as Iranian weapons. Dozens of warplanes, including F-35s and F-15s, participated in the long-distance mission, one Israel's most complicated operations. Yemen's health ministry reported that six people were killed.
July 21: The Houthis launched a missile toward Eilat, but Israel intercepted it.
Related Material:

The Islamists
Learn more about Hamas and how it relates to similarly aligned organizations throughout the region. Read more

Explore More
Browse Insights & Analysis
Israel Escalates Attacks in Gaza: What’s Next?

The Gaza Ceasefire and Its Aftermath: Danger and Opportunity